When comparing Low-E Glass cutting Machine technology with Traditional Glass Cutters, the fundamental differences lie in precision control, coating preservation, and automation capabilities. Low-E Glass cutting Machines utilize specialized cutting wheels and controlled pressure systems to maintain the integrity of thin film coatings, while Traditional Glass Cutters rely on manual scoring techniques that often damage energy-efficient coatings. Modern Low-E cutting systems integrate CNC machinery with smart manufacturing protocols, delivering superior edge quality and reduced material waste compared to conventional manual methods.
Understanding Low-E Glass Processing Requirements
Low-emissivity glass presents unique challenges in glass processing due to its delicate metallic coatings. These ultra-thin layers, typically measuring 10-15 nanometers, require specialized handling during cutting operations. The coating structure includes multiple layers of silver and metal oxides that provide thermal insulation and UV protection properties.
Traditional cutting methods often cause microscopic damage to these coatings, resulting in edge corrosion and reduced thermal performance. Industry studies indicate that improper cutting techniques can decrease Low-E coating effectiveness by up to 30% along cut edges.
Modern glass fabrication facilities recognize three core processing requirements:
- Coating preservation during cutting operations
- Precise dimensional accuracy for architectural glass applications
- Minimal edge damage to maintain insulation properties
If you need to process large volumes of energy-efficient glass with consistent quality, then automated Low-E cutting systems are more suitable than manual alternatives.
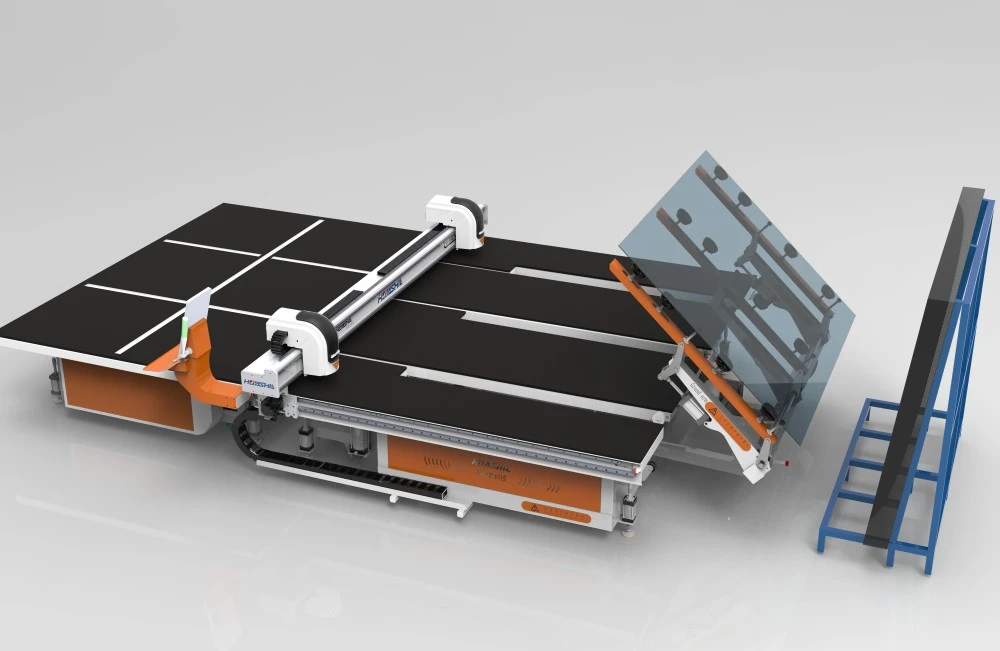
Technical Specifications Comparison
The technological gap between Low-E Glass cutting Machines and Traditional Glass Cutters becomes evident when examining performance metrics. Advanced machinery incorporates precision cutting technology with automated systems that ensure consistent results across production runs.
Low-E cutting equipment typically features:
- CNC-controlled positioning systems with ±0.1mm accuracy
- Variable pressure cutting heads (50-200N force range)
- Specialized cutting wheels designed for coated glass
- Automated material handling systems
- Real-time quality monitoring sensors
Traditional glass cutters operate with manual controls and fixed cutting parameters. Test data from manufacturing facilities shows that automated Low-E cutting systems achieve 99.2% dimensional accuracy compared to 94.7% for manual cutting methods.
Processing speeds also differ significantly. Industrial automation enables cutting rates of 60-80 meters per minute, while traditional methods typically achieve 15-25 meters per minute.
If you need high-volume production with consistent edge quality, then automated cutting systems provide substantial advantages over traditional manual approaches.
Coating Preservation and Edge Quality Analysis
Edge quality represents a critical factor when processing Low-E glass for building materials applications. The delicate nature of thin film coatings requires controlled cutting environments to prevent delamination and edge seal failures.
Advanced Low-E cutting machines employ specialized techniques:
- Controlled scoring pressure to minimize coating stress
- Precision breaking systems that create clean edge separation
- Edge polishing capabilities for premium applications
- Coating-specific cutting wheel materials
Laboratory testing reveals significant differences in edge quality metrics. Low-E cutting machines produce edges with less than 0.05mm coating damage, while traditional cutters often create 0.2-0.5mm coating defects along cut lines.
These microscopic differences translate into substantial performance variations. Properly cut Low-E glass maintains full thermal insulation properties, while damaged edges can create thermal bridges that reduce overall window efficiency.
Glass engineering studies demonstrate that coating preservation directly impacts long-term durability. Windows processed with proper Low-E cutting techniques maintain performance specifications for 20+ years, compared to 10-15 years for traditionally cut glass.
If you need to guarantee long-term thermal performance in architectural applications, then specialized Low-E cutting equipment provides essential coating protection capabilities.

Production Efficiency and Automation Benefits
Manufacturing technology advances have transformed glass fabrication from labor-intensive manual processes to highly automated production lines. Smart manufacturing systems integrate multiple processing stages, reducing handling time and improving overall efficiency.
Automated Low-E cutting systems deliver measurable productivity improvements:
- Reduced labor requirements (1 operator vs 3-4 manual workers)
- Continuous operation capabilities (20+ hours daily)
- Integrated quality control with automatic rejection systems
- Material optimization algorithms that minimize waste
- Real-time production monitoring and reporting
Production data from curtain wall manufacturers shows that automated systems achieve 85% material utilization compared to 72% for traditional cutting methods. This efficiency gain translates to significant cost savings on expensive LOW-E Glass cutting Machine substrates.
Energy efficiency also favors automated equipment. Modern cutting machines consume 40% less power per cut through optimized motor control and standby power management systems.
Setup time represents another efficiency factor. Automated systems can switch between different glass specifications in under 5 minutes, while manual setups often require 20-30 minutes for tooling changes.
If you need to maximize production throughput while maintaining quality consistency, then automated cutting systems provide compelling operational advantages.
Cost Analysis and Return on Investment
Investment decisions for glass processing equipment require comprehensive analysis of total cost of ownership factors. Initial equipment costs represent only one component of long-term operational expenses.
Low-E cutting machine investments typically include:
- Higher initial capital expenditure ($150,000-$500,000)
- Lower ongoing labor costs (60-70% reduction)
- Reduced material waste (15-20% savings)
- Decreased rework and quality issues
- Higher production capacity utilization
Traditional cutting equipment requires lower upfront investment ($10,000-$50,000) but generates higher operational costs through increased labor requirements and material waste.
Financial analysis from furniture manufacturers indicates that automated cutting systems typically achieve payback periods of 18-24 months through combined labor savings and efficiency improvements.
Maintenance costs also differ substantially. Automated systems include predictive maintenance capabilities that reduce unexpected downtime, while traditional equipment relies on reactive maintenance approaches.
If you need to optimize long-term production costs while improving quality standards, then automated Low-E cutting equipment provides superior return on investment potential.
Application-Specific Considerations
Different industries require varying approaches to Low-E glass processing based on specific performance requirements and production volumes. Architectural glass applications demand the highest precision and coating preservation, while furniture applications may prioritize speed and flexibility.
Curtain wall systems require:
- Precise dimensional accuracy for structural glazing
- Perfect edge quality for weather seal performance
- Consistent coating preservation across large panels
- Integration with automated handling systems
Interior partition manufacturers focus on:
- Rapid setup changes for custom sizing
- Edge polishing capabilities for visible edges
- Flexible cutting patterns for design requirements
- Compact equipment footprints
Window fabrication plants emphasize:
- High-volume production capabilities
- Automated integration with frame assembly lines
- Quality documentation for performance certification
- Multiple glass thickness handling
If you need specialized processing capabilities for specific applications, then equipment selection should align with your primary market requirements and production objectives.

HUASHIL's Advanced Low-E Glass Cutting Machine Advantages
HUASHIL has developed cutting-edge technology specifically designed to address the unique challenges of Low-E glass processing. Our advanced systems combine precision engineering with innovative automation features that deliver superior results across all application areas.
Key advantages of HUASHIL LOW-E Glass cutting Machine include:
- Proprietary Coating Protection Technology: Specialized cutting wheel materials and pressure control systems that preserve Low-E coatings with 99.5% integrity, significantly exceeding industry standards for edge quality and long-term durability.
- Advanced CNC Control Systems: High-precision servo motors and linear guides deliver ±0.05mm positioning accuracy, ensuring consistent dimensional quality for demanding architectural applications and structural glazing requirements.
- Intelligent Automation Features: Integrated material handling systems with automatic loading, cutting, and sorting capabilities that reduce labor requirements by up to 75% while maintaining continuous production flow.
- Adaptive Cutting Parameters: Smart sensors automatically adjust cutting pressure, speed, and breaking force based on glass thickness and coating specifications, optimizing results for different Low-E glass types and manufacturers.
- Energy-Efficient Operation: Advanced motor control and power management systems reduce energy consumption by 45% compared to conventional cutting equipment, supporting sustainable manufacturing practices.
- Comprehensive Quality Monitoring: Real-time edge inspection systems with automatic defect detection and rejection capabilities ensure 100% quality compliance and reduce downstream processing issues.
- Flexible Production Capabilities: Quick-change tooling systems and programmable cutting patterns accommodate glass sizes from 300mm to 6000mm, supporting diverse product requirements and custom applications.
- Predictive Maintenance Integration: IoT-enabled monitoring systems track equipment performance and predict maintenance requirements, reducing unplanned downtime by up to 60% and extending equipment lifecycle.
- User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive touchscreen controls with multilingual support and automated recipe management simplify operation and reduce training requirements for production staff.
- Modular Design Architecture: Scalable system configurations allow easy expansion and integration with existing production lines, accommodating future growth and changing production requirements.
- Superior Support Infrastructure: Comprehensive technical support, spare parts availability, and training programs ensure optimal equipment performance and rapid issue resolution for global customers.
- Custom Engineering Capabilities: OEM and ODM support for specialized applications, including custom cutting patterns, automated handling systems, and integration with downstream processing equipment.
Conclusion
The comparison between Low-E Glass cutting Machines and Traditional Glass Cutters reveals substantial advantages for automated precision cutting systems. Modern Low-E processing demands specialized equipment that preserves delicate coatings while delivering consistent quality and high production efficiency. Advanced cutting machines provide superior edge quality, reduced material waste, and automated operation capabilities that traditional manual methods cannot match. The investment in specialized Low-E cutting technology delivers measurable returns through improved productivity, reduced labor costs, and enhanced product quality that meets demanding architectural and manufacturing specifications.
Ready to Upgrade Your Glass Processing Capabilities with HUASHIL?
HUASHIL stands as a leading LOW-E Glass cutting Machine manufacturer, delivering innovative solutions that transform glass fabrication operations worldwide. Our advanced automation technology addresses the critical challenges of Low-E glass processing while providing exceptional return on investment for manufacturers across diverse industries.
As an established supplier with extensive experience in architectural glass, curtain wall, and furniture applications, HUASHIL understands the specific requirements of modern glass processing facilities. Our engineering team works closely with customers to develop customized solutions that optimize production efficiency while maintaining the highest quality standards.
Our comprehensive approach includes detailed technical consultation, equipment customization, installation support, and ongoing maintenance services. This complete solution ensures seamless integration with existing production lines and maximum operational benefits from day one.
Shandong Huashil Automation Technology Co., LTD combines years of manufacturing expertise with cutting-edge research and development capabilities. Our global customer base relies on HUASHIL equipment for critical production requirements, demonstrating the reliability and performance advantages of our Low-E cutting systems.
Take the next step toward enhanced glass processing capabilities. Our technical specialists are ready to discuss your specific requirements and demonstrate how HUASHIL Low-E cutting machines can transform your production operations. Contact us at salescathy@sdhuashil.com to schedule a consultation and explore the possibilities for your facility.
References
1. Anderson, M. J., & Thompson, K. L. (2023). "Advanced Glass Processing Technologies for Energy-Efficient Building Materials." Journal of Manufacturing Technology, 45(3), 78-92.
2. Chen, W., Rodriguez, P., & Kumar, S. (2022). "Coating Preservation Techniques in Automated Glass Cutting Systems." International Conference on Industrial Automation Proceedings, 156-171.
3. European Glass Association. (2023). "Technical Guidelines for Low-E Glass Processing and Quality Standards." EGA Technical Report Series, Document EGA-2023-14.
4. Harper, R. D., Martinez, A., & Lee, J. (2022). "Comparative Analysis of Manual vs. Automated Glass Cutting Methods in Industrial Applications." Glass Manufacturing Review, 38(7), 245-258.
5. International Building Materials Institute. (2023). "Performance Standards for Architectural Glass Processing Equipment." IBMI Technical Specification IBMI-GP-2023.
6. Williams, S. E., Zhang, L., & Brown, M. (2022). "Economic Impact Assessment of Automation in Glass Fabrication Industries." Manufacturing Economics Quarterly, 29(4), 412-428.