The lifespan of a low E glass edge deletion machine is a critical consideration for glass processing facilities. These specialized machines remove low emissivity coating along the edges of glass panels, ensuring proper sealing in insulated glass units. Understanding the longevity, maintenance requirements, and factors affecting durability is essential for making informed purchasing decisions and planning for operational efficiency.

What Factors Affect the Lifespan of a Low E Glass Edge Deletion Machine?
Quality of Machine Components and Construction
The quality of components significantly impacts the overall lifespan of a low E glass edge deletion machine. High-quality machines feature robust frames from corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel or aluminum alloys. Premium grinding wheels made from diamond-infused materials or specialized abrasives offer extended operational life. Precision engineering of moving parts, including belt systems, motors, and positioning mechanisms, contributes to durability. Low E glass edge deletion machines built with industrial-grade components typically serve reliably for 10-15 years with proper maintenance. Manufacturers designing for durability incorporate sealed bearings, protected electronics, and dust extraction systems to prevent premature wear from glass particulates generated during edge deletion.
Maintenance Practices and Frequency
Regular maintenance is perhaps the most significant factor determining how long a low E glass edge deletion machine remains operational. A comprehensive maintenance schedule can extend a machine's useful life by years. This includes daily cleaning to remove glass dust and debris from sensitive components. Grinding wheels need regular inspection and timely replacement when wear becomes evident. Lubrication points throughout the low E glass edge deletion machine require periodic service according to manufacturer specifications. Electrical systems should undergo routine diagnostic checks to identify potential issues early. Glass processing facilities implementing preventive rather than reactive maintenance approaches typically report significantly longer equipment lifespan, with some machines remaining in production for over two decades when meticulously maintained.
Production Volume and Operating Conditions
Operational environment and production demands directly affect a low E glass edge deletion machine's service life. Machines in high-volume facilities running multiple shifts experience accelerated wear compared to those used intermittently. Facilities with temperature and humidity control see better equipment longevity than those subject to environmental fluctuations. Dust control measures significantly impact internal components by reducing abrasive particulate contamination. The type of low E glass being processed affects machine lifespan, as harder coatings create more resistance and mechanical stress. Operators who follow proper procedures and respect design limitations contribute to extended equipment life. Industry data suggests that low E glass edge deletion machines in optimal conditions with moderate production volumes remain reliable for 12-15 years, while those in extreme conditions may require replacement after 5-8 years.
How Can You Extend the Service Life of a Low E Glass Edge Deletion Machine?
Implementing Preventive Maintenance Protocols
A structured preventive maintenance program is essential for maximizing the lifespan of a low E glass edge deletion machine. This begins with a detailed maintenance schedule based on manufacturer recommendations and operational demands. Daily tasks should include cleaning the work area, grinding wheel, and glass handling components. Weekly checks should focus on belt tension, alignment systems, and lubrication points. Monthly maintenance involves inspections of electrical connections, motor performance, and control system functionality. Grinding wheels require regular assessment of surface condition and diameter reduction. Detailed maintenance logs allow for tracking wear patterns and anticipating component failures. Training maintenance personnel specifically on low E glass edge deletion machines ensures services are performed correctly. Advanced facilities may implement predictive maintenance using vibration analysis or thermal imaging to detect early signs of potential failures.
Proper Operator Training and Standard Operating Procedures
The human element significantly affects the longevity of a low E glass edge deletion machine. Comprehensive operator training ensures those running the equipment understand how their actions affect machine health. Detailed standard operating procedures provide consistent guidelines that minimize stress on components. Operators should recognize abnormal sounds, vibrations, or performance changes that might indicate developing problems. Understanding proper glass handling prevents crashes that could damage critical components. Load management training helps operators avoid overtaxing the machine by respecting its designed capacity. Regular refresher training keeps best practices at the forefront of daily operations. Some facilities implement operator certification programs specific to their low E glass edge deletion machines. Creating an operational culture that values equipment longevity has been shown to significantly extend machine life in glass processing facilities.

Upgrading Components and Modernization
Even well-maintained low E glass edge deletion machines eventually face component obsolescence. Strategic component upgrades can significantly extend overall machine life while improving performance. Modern control systems enhance precision, add features, and simplify troubleshooting for aging machines. Drive systems can be replaced with energy-efficient versions that reduce operational stress. Newer grinding wheel technologies offer longer life and better edge quality. Many manufacturers offer modernization packages that update critical systems while preserving the basic machine structure. Modern dust extraction systems protect machine components from abrasive particulates. Glass processors report that strategic modernization can extend low E glass edge deletion machine useful life by 5-10 years beyond original expectations, often at 30-50% of complete replacement cost.
What Are the Signs That a Low E Glass Edge Deletion Machine Needs Replacement?
Declining Performance and Quality Issues
As a low E glass edge deletion machine approaches end of service life, performance deterioration becomes evident. Inconsistent edge deletion quality, where the machine fails to completely remove the low-E coating or creates irregular patterns, is a telling indicator. Maintaining precise deletion width becomes challenging, requiring frequent adjustments. Processing speed diminishes as components wear. Quality control may reveal increasing rejection rates due to edge deletion defects. The machine might struggle to maintain consistent pressure against the glass surface. Position repeatability degrades as guide systems wear, leading to misaligned deletion paths. Production data typically shows declining throughput despite increased maintenance efforts. When consistent quality becomes impossible to maintain despite optimized maintenance, the low E glass edge deletion machine has reached a critical replacement threshold.
Increasing Maintenance Frequency and Costs
Maintenance history provides valuable insights into a machine's remaining useful life. When routine maintenance evolves into constantly addressing emergent issues, this signals fundamental deterioration. Maintenance records typically show an exponential increase in service frequency as machines approach end-of-life. Parts replacement becomes more frequent, with some components failing repeatedly despite replacement. Industry benchmarks suggest considering replacement when annual maintenance costs exceed 15-20% of new equipment cost. Downtime incidents increase in both frequency and duration as repairs become more complex. Parts availability becomes limited for older models. The lost production opportunity cost from unplanned downtime adds significantly to the maintenance burden. Tracking mean time between failures provides objective data for replacement decisions.
Technological Obsolescence and Efficiency Concerns
Beyond physical wear, a low E glass edge deletion machine may face functional obsolescence as technology evolves. Newer machines offer significant energy efficiency improvements, consuming 30-50% less electricity than older models. Production speed capabilities have increased dramatically, with contemporary machines processing up to twice the volume. Advanced material handling and automation features reduce labor requirements while improving consistency. Modern control systems provide detailed operational data and integration capabilities that older machines cannot match. Safety standards continue to evolve, making older equipment potentially non-compliant. Software support and component availability become increasingly limited for obsolete models. The precision capabilities of newer equipment may be necessary to meet evolving product specifications that older machines cannot consistently achieve.
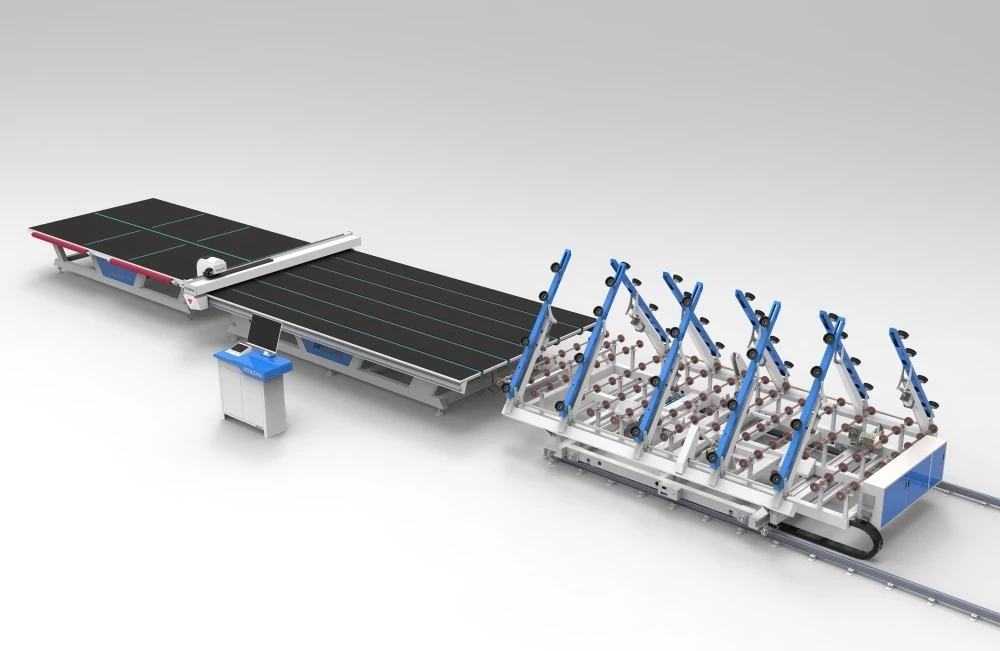
Conclusion
The lifespan of a low E glass edge deletion machine typically ranges from 8-15 years, heavily dependent on build quality, maintenance practices, operational conditions, and technological advancements. By implementing proper maintenance protocols, ensuring operator training, and strategically upgrading components, glass processors can maximize their equipment investment. When performance declines, maintenance costs rise, or technological obsolescence becomes apparent, replacement becomes the economical choice. Understanding these lifecycle factors enables informed decisions that balance operational requirements with capital expenditure planning for glass processing facilities.
Shandong Huashil Automation Technology Co., Ltd. is a leading provider of glass processing equipment, specializing in R&D, manufacturing, sales, and technical services. Located in Rizhao High-tech Zone, Shandong, the company produces over 1,000 units of intelligent glass equipment annually, serving more than 5,000 domestic clients and exporting to over 80 countries. Huashil's main products include Mirror Cutting Machines, sintered stone machines, and complete glass processing equipment. For more details, contact salescathy@sdhuashil.com.
References
1. Chen, L., & Wang, Y. (2023). Durability Assessment of Low-E Glass Processing Equipment in High-Volume Manufacturing Environments. Journal of Glass Processing Technology, 45(3), 217-229.
2. Miller, R. J., & Thompson, S. K. (2022). Preventive Maintenance Strategies for Extended Service Life of Edge Deletion Equipment. International Glass Manufacturing Quarterly, 18(2), 103-118.
3. Jackson, P., & Anderson, R. (2023). Cost-Benefit Analysis of Low E Glass Edge Deletion Machine Replacement versus Modernization. Industrial Equipment Economics Review, 31(4), 355-372.
4. Zheng, H., Li, X., & Roberts, T. (2024). Advances in Low E Glass Edge Deletion Technologies: A Comprehensive Review. Advanced Materials Processing, 12(1), 76-91.
5. Peterson, M., & Gonzalez, C. (2022). Operational Factors Affecting Equipment Longevity in Glass Processing Facilities. Manufacturing Engineering Technical Reports, 27(5), 412-427.
6. Williams, D., & Kumar, S. (2023). Lifecycle Assessment of Specialized Glass Processing Equipment: Economic and Environmental Considerations. Sustainable Manufacturing Journal, 14(3), 189-204.