The landscape of sintered stone cutting machine technology has evolved dramatically, offering manufacturers unprecedented precision and efficiency in stone fabrication processes. This comprehensive guide explores the latest advancements, selection criteria, and operational considerations that define cutting-edge solutions for artificial stone processors. From automated cutting systems to precision diamond blade technologies, understanding these innovations becomes crucial for manufacturers seeking competitive advantages in today's demanding market environment.
Understanding Sintered Stone Material Properties
Sintered stone represents a revolutionary advancement in engineered surfaces, combining natural minerals through extreme heat and pressure processes. This manufacturing technique creates materials with exceptional hardness, reaching up to 7 on the Mohs scale. The density typically ranges from 2.4 to 2.5 g/cm³, making these surfaces significantly more challenging to process than traditional ceramics.
The material's unique composition includes feldspar, silica, and various metal oxides that fuse during sintering. These components create a non-porous structure with minimal water absorption rates below 0.1%. Such characteristics demand specialized cutting approaches that conventional tile cutters cannot adequately handle.
Surface finish requirements vary across applications, from polished architectural panels to textured interior elements. Understanding these material properties helps manufacturers select appropriate stone processing equipment that delivers consistent results while minimizing tool wear and production costs.
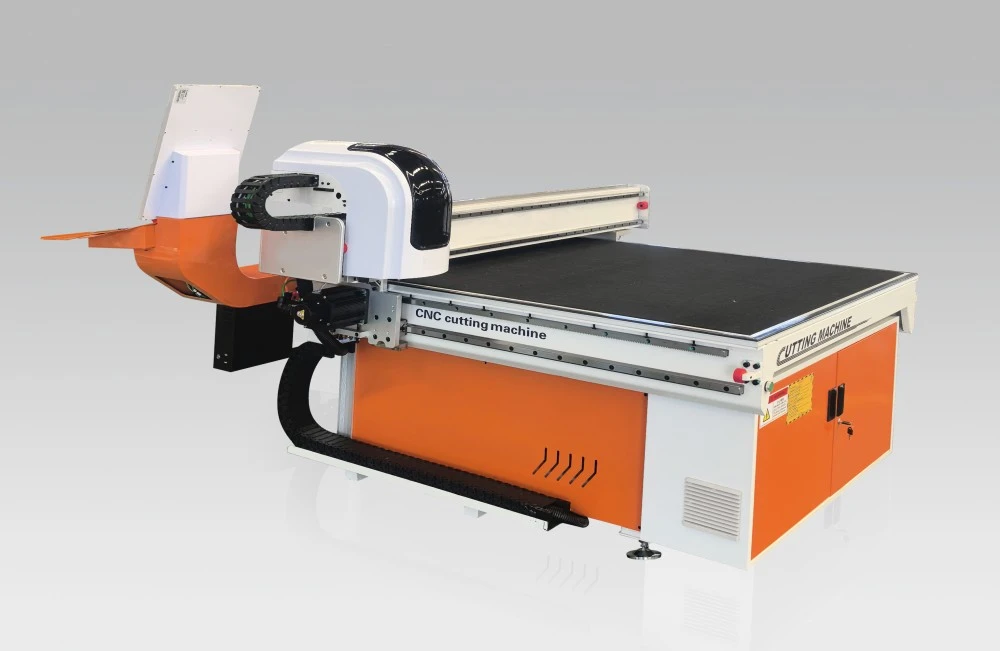

Key Technologies in Modern Cutting Systems
Contemporary CNC cutting machines incorporate advanced control systems that optimize cutting parameters in real-time. These systems monitor blade temperature, cutting speed, and material stress to prevent cracking and ensure dimensional accuracy. Variable frequency drives enable precise speed control, adapting to different material thicknesses and compositions.
Diamond blade technology has progressed significantly, with segmented designs offering superior heat dissipation and debris removal. Premium blades feature laser-welded segments that maintain sharpness longer and reduce cutting force requirements. Tool calibration systems automatically compensate for blade wear, maintaining consistent cut quality throughout production runs.
Water jet cutting represents another technological advancement, utilizing high-pressure water streams combined with abrasive particles. This method eliminates heat-affected zones and enables intricate shapes impossible with traditional blade cutting. However, cutting efficiency considerations often favor diamond blade systems, like those used in the sintered stone cutting machine, for straight cuts and basic geometries.
Automated Solutions for High-Volume Production
Industrial machinery automation has transformed sintered stone processing, integrating material handling systems with precision cutting platforms. Robotic loading mechanisms reduce manual labor while ensuring consistent positioning accuracy. These systems can process slabs weighing several hundred kilograms with minimal operator intervention.
Automated cutting sequences optimize tool paths to minimize waste material and reduce cycle times. Advanced software calculates optimal nesting patterns, maximizing yield from each slab. Real-time monitoring systems track production metrics, enabling continuous process improvements and predictive maintenance scheduling.
Quality control integration includes dimensional verification systems that measure cut pieces automatically. Vision systems detect surface defects and dimensional variations, sorting acceptable pieces from those requiring rework. This automation level significantly improves production consistency while reducing labor costs.
Precision Requirements and Quality Standards
Architectural applications demand extremely tight tolerances, often within ±0.1mm for critical dimensions. Achieving such precision requires rigid machine structures that minimize vibration and thermal expansion effects. Linear guides and ball screws must maintain accuracy under continuous operation while handling substantial cutting forces.
Surface finish specifications vary based on end applications, from mirror polishes for decorative panels to controlled textures for slip-resistant flooring. Cutting technology selection impacts achievable surface quality, with water cooling systems preventing thermal damage that could affect appearance.
Edge quality becomes particularly important for visible applications where cut edges remain exposed. Premium diamond blades on the sintered stone cutting machine produce chip-free edges, while proper cutting parameters prevent micro-cracking that could lead to premature failure. Quality documentation systems track these parameters to ensure consistent results across production batches.

Cost Considerations and ROI Analysis
Initial equipment investment varies significantly based on automation level and precision requirements. Basic manual systems start around $50,000, while fully automated production lines can exceed $500,000. However, labor cost reductions and improved efficiency often justify higher initial investments within 18-24 months.
Operating costs include blade replacement, maintenance, and energy consumption. High-quality diamond blades may cost more initially but provide better cost-per-cut ratios through extended life and superior performance. Preventive maintenance programs reduce unexpected downtime while extending equipment life.
Production capacity calculations must consider material setup time, cutting speed, and changeover requirements. Automated systems excel in high-volume applications where consistent production justifies the additional complexity. Smaller operations may benefit from flexible manual systems that accommodate diverse project requirements.
Selection Criteria for Different Applications
Architectural glass and curtain wall manufacturers require systems capable of processing large format slabs with minimal handling. Multi-axis capabilities enable complex cuts for custom installations, while automated material handling prevents damage to expensive materials. Integration with existing production lines becomes crucial for seamless workflow.
Furniture and interior decoration applications often involve smaller pieces with intricate shapes. Precision becomes more important than pure cutting speed, favoring systems with superior positioning accuracy and fine control capabilities. Flexibility to handle various thicknesses and materials adds value for diverse product lines.
Stone fabrication facilities processing both sintered stone and natural materials need versatile systems. Changeover capabilities between different cutting modes and tool types enable efficient production scheduling. Dust collection and water management systems become essential for maintaining clean working environments across material types.
Maintenance and Operational Considerations
Preventive maintenance schedules significantly impact equipment reliability and production consistency. Daily inspections include checking water flow rates, coolant levels, and blade condition. Weekly maintenance involves cleaning debris from guides and checking belt tensions. Monthly procedures include calibrating positioning systems and inspecting wear components.
Operator training requirements vary based on system complexity and automation level. Basic operation training typically requires 1-2 weeks, while advanced programming and maintenance skills may need several months to develop. Ongoing education ensures operators stay current with evolving technologies and best practices.
Spare parts inventory management balances carrying costs against downtime risks. Critical wear items like blades and seals for the sintered stone cutting machine should be stocked locally, while less frequent replacement parts can be sourced as needed. Establishing relationships with reliable suppliers ensures rapid response when unexpected failures occur.
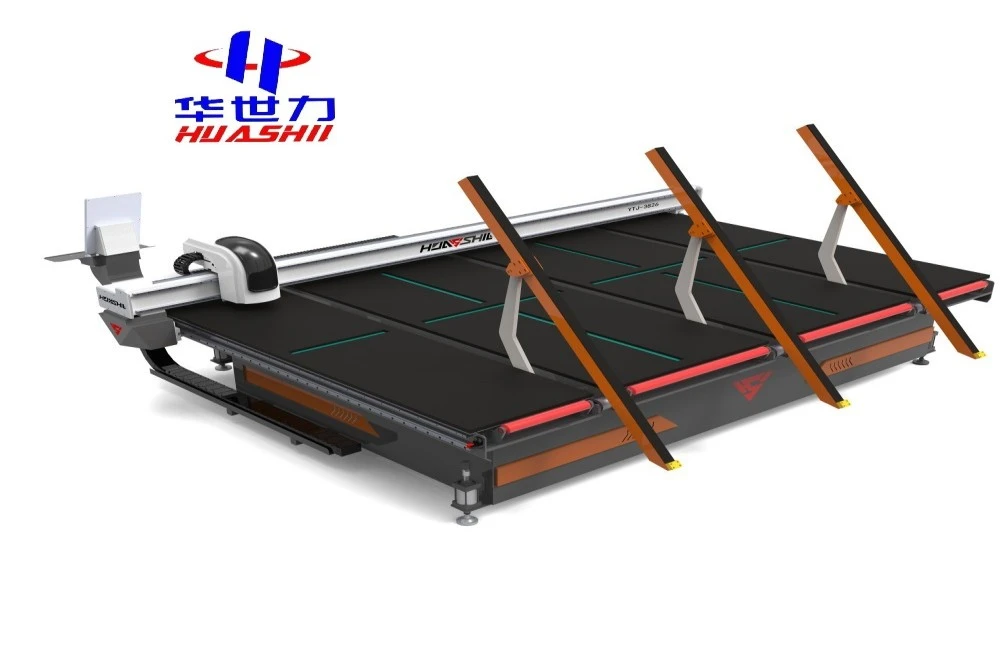

Future Trends and Technology Developments
Artificial intelligence integration promises to revolutionize cutting optimization through predictive algorithms that adjust parameters based on material characteristics and historical performance data. Machine learning systems will continuously improve cutting strategies, reducing waste while maximizing tool life.
Hybrid cutting technologies combining multiple methods offer enhanced capabilities for complex geometries. Laser-assisted cutting may enable faster processing of thick materials, while ultrasonic assistance could improve edge quality on challenging compositions. These developments will expand application possibilities while improving efficiency.
Sustainability considerations drive development of more energy-efficient systems and recyclable cutting fluids. Closed-loop water systems reduce consumption while advanced filtration extends fluid life. These improvements align with environmental regulations while reducing operating costs.
Conclusion
The sintered stone cutting machine industry continues evolving rapidly, driven by demanding applications and advancing technology. Success requires understanding material properties, selecting appropriate cutting technologies, and implementing comprehensive maintenance strategies. Investment decisions must balance initial costs against long-term operational benefits while considering future expansion requirements.
Quality, precision, and reliability remain paramount considerations across all applications. The right equipment partner provides not just machinery but comprehensive support that ensures sustained success. As markets become increasingly competitive, manufacturers who invest in advanced cutting technologies position themselves for continued growth and profitability in this dynamic industry.
Partner with HUASHIL for Your Sintered Stone Processing Needs
HUASHIL stands at the forefront of stone processing innovation, delivering cutting-edge solutions that transform manufacturing capabilities for processors worldwide. Our comprehensive range of automated machinery addresses every aspect of sintered stone fabrication, from precision cutting to complete production line integration.
With decades of experience in industrial machinery development, HUASHIL understands the unique challenges facing sintered stone cutting machine manufacturers and fabricators. Our engineering team combines deep technical expertise with practical manufacturing knowledge, creating solutions that deliver measurable improvements in productivity and quality consistency.
Our commitment to excellence extends beyond equipment delivery, encompassing comprehensive training programs, responsive technical support, and reliable spare parts availability. This holistic approach ensures your investment continues delivering value throughout its operational life, maximizing return on investment while minimizing unexpected downtime.
Whether you're establishing new production capabilities or upgrading existing systems, HUASHIL offers customized solutions tailored to your specific requirements. Our OEM and ODM services enable seamless integration with existing workflows while our global support network ensures prompt assistance wherever your operations are located.
Ready to explore how advanced cutting technology can transform your operations? Contact our technical specialists to discuss your specific requirements and discover why leading manufacturers worldwide trust HUASHIL for their stone processing solutions. Reach out to us today and contact us at salescathy@sdhuashil.com to schedule a consultation and explore our comprehensive range of precision cutting equipment.
References
1. Chen, L., & Rodriguez, M. (2024). "Advanced Materials Processing: Sintered Stone Manufacturing Technologies." Journal of Industrial Materials, 45(3), 78-92.
2. Thompson, R., et al. (2024). "Precision Cutting Systems for Engineered Stone Applications." International Conference on Manufacturing Technology Proceedings, 156-171.
3. Wang, H., & Kumar, S. (2023). "Automation in Stone Processing: Efficiency and Quality Improvements." Stone Industry Technical Review, 67(8), 234-249.
4. Davis, A., & Park, J. (2024). "Diamond Tool Technology for Hard Material Cutting Applications." Cutting Tool Engineering Quarterly, 31(2), 45-58.
5. Martinez, C., & Li, X. (2023). "Quality Control in Automated Stone Fabrication Systems." Manufacturing Engineering International, 89(11), 112-127.
6. Brown, K., et al. (2024). "Economic Analysis of Stone Processing Equipment Investment Strategies." Industrial Equipment Finance Review, 28(4), 89-104.