The 5133 glass cutting line is a sophisticated piece of equipment widely used in glass manufacturing facilities for precision cutting operations. Despite its advanced design and functionality, operators and maintenance teams often encounter several common issues that can impact production efficiency, cutting quality, and equipment longevity. This article explores the most frequent challenges associated with the 5133 glass cutting line and provides practical troubleshooting strategies to address them effectively.
Why is the 5133 glass cutting line experiencing inconsistent cutting accuracy?
Calibration and Alignment Problems
Calibration and alignment issues are primary culprits behind inconsistent cutting accuracy in the 5133 glass cutting line. When the machine's positioning system becomes misaligned even by fractions of a millimeter, it can result in significant deviations in the final cut products. The optical recognition system requires precise calibration to maintain cutting tolerances within acceptable ranges. Regular maintenance checks often reveal that positioning sensors have gradually drifted from optimal settings due to vibration and continuous operation.
The solution involves implementing a comprehensive calibration schedule that includes verifying alignment parameters weekly and performing full calibrations monthly. Advanced facilities have found that integrating digital calibration tools with the 5133 glass cutting line's control system can automate this process, reducing human error and ensuring more consistent results. Installing vibration dampening mounts beneath critical components has proven effective in maintaining calibration for longer periods.
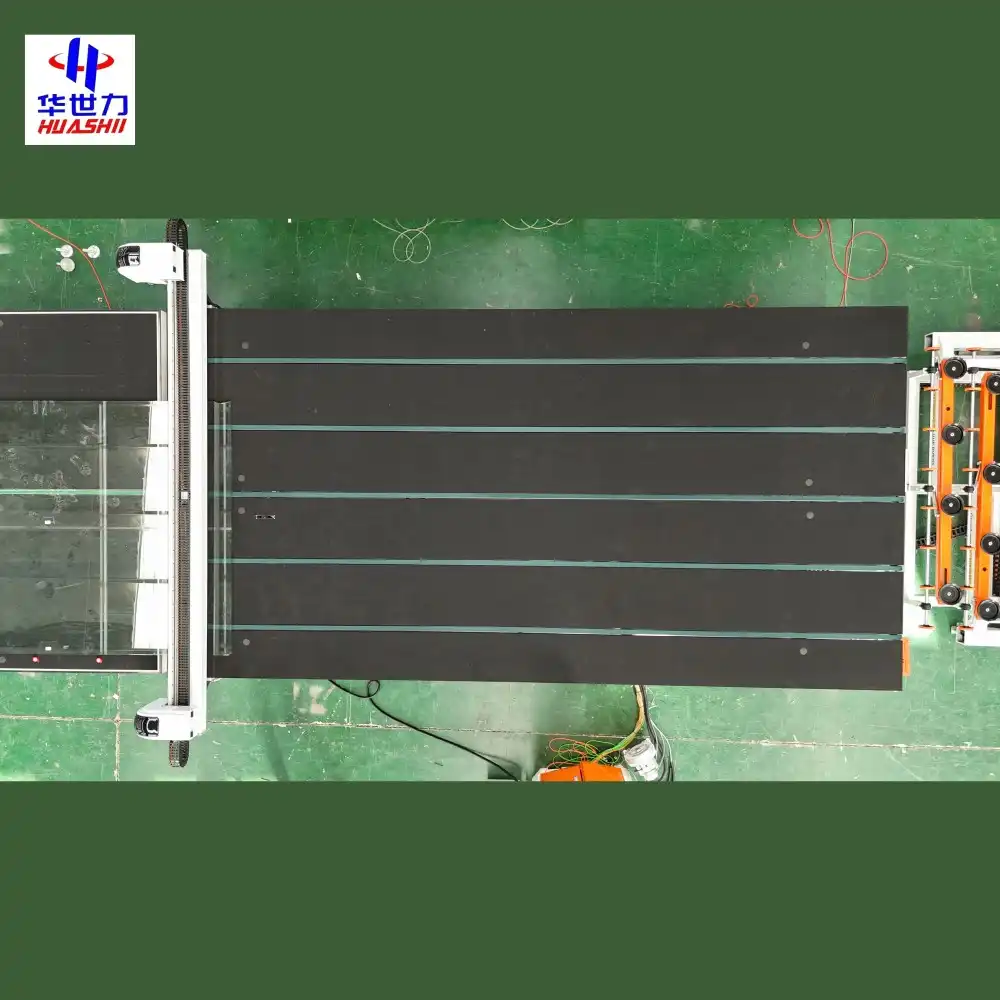
Cutting Tool Degradation
Over time, the cutting wheels and associated tools on the 5133 glass cutting line inevitably wear down, leading to changes in cutting performance. When these tools degrade, they cannot maintain the precise scoring depth required for clean breaks, resulting in inconsistent cut quality or breakage during separation. Most operators miss early warning signs of tool wear, such as increased cutting pressure requirements or subtle changes in the acoustic signature during operation.
Implementing a proactive replacement schedule based on the number of linear meters cut, rather than waiting for visible defects, can significantly improve consistency. Modern 5133 glass cutting line installations often incorporate automated tool monitoring systems that track wear patterns and alert maintenance teams when replacements are needed. These systems analyze cutting force data and can detect changes that human operators might miss until quality problems have already appeared.
Software and Control System Issues
The sophisticated control systems that govern the 5133 glass cutting line's operation can sometimes develop glitches or configuration errors that affect cutting accuracy. These software-related issues may manifest as random deviations in cutting paths, incorrect interpretation of cutting templates, or communication breakdowns between different modules of the system.
When troubleshooting inconsistent accuracy, technicians should verify that all control system components are running the most current firmware versions and that communication protocols between subsystems are functioning correctly. Creating regular system backups of the 5133 glass cutting line's configuration settings provides a reliable restoration point when anomalies occur. Maintaining a comprehensive log of software updates helps identify potential correlation between system modifications and the onset of accuracy issues. Some manufacturers have developed specialized diagnostic software for the 5133 glass cutting line that can run comprehensive system checks and identify potential software conflicts before they impact production quality.
How can the 5133 glass cutting line's operational speed be optimized without compromising quality?
Acceleration and Deceleration Profile Adjustments
Fine-tuning the acceleration and deceleration profiles of the 5133 glass cutting line can dramatically impact both operational speed and cutting quality. Every glass type and thickness responds differently to various cutting speeds, and finding the optimal balance requires methodical testing and adjustment. The standard settings provided by manufacturers are typically conservative to accommodate a wide range of glass types.
By creating custom acceleration curves tailored to particular glass specifications, operators can achieve significantly higher throughput without sacrificing edge quality. Advanced users of the 5133 glass cutting line have developed material-specific profiles that maximize cutting speed during straight sections while appropriately reducing velocity for complex contours and corners. Some facilities have reported speed improvements of up to 30% using this systematic approach, while maintaining or even improving cut quality metrics.
Optimizing Material Handling Systems
The material handling components of the 5133 glass cutting line often create bottlenecks that limit overall system throughput more than the actual cutting speed. The 5133 glass cutting line's performance is only as strong as its weakest link, which frequently turns out to be glass loading, positioning, or offloading systems rather than the cutting mechanism itself.
By analyzing the complete production cycle, technicians can identify where the 5133 glass cutting line spends excessive time waiting for auxiliary operations to complete. Upgrading pneumatic systems to provide faster actuation, implementing parallel processing where possible, and ensuring optimal vacuum strength for secure glass holding can all contribute to faster cycle times. Some manufacturers have modified their installations by adding buffer zones before and after the cutting station, allowing continuous operation even during sheet changeovers.

Cutting Sequence Optimization
The order and pattern in which cuts are executed on the 5133 glass cutting line can significantly impact overall production speed. Most basic implementations follow simple geometric patterns when executing cutting plans, which can result in excessive tool movement across the glass surface. Advanced optimization algorithms analyze the entire cutting pattern to determine the most efficient path, minimizing the total distance traveled by the cutting head.
This approach can reduce non-productive movement time by up to 40% on complex jobs processed through the 5133 glass cutting line. Furthermore, intelligent sequencing considers structural stability during the cutting process, ensuring that the glass sheet maintains sufficient integrity throughout the operation. Some facilities have implemented custom optimization modules that interact with their design software, automatically adjusting cutting sequences based on glass type, thickness, and the specific layout of parts.
What maintenance procedures extend the lifespan of the 5133 glass cutting line?
Preventive Lubrication and Cleaning Protocols
Implementing rigorous lubrication and cleaning schedules is fundamental to extending the operational lifespan of the 5133 glass cutting line. Glass dust and debris create significant challenges for the precision components of the machine, accelerating wear and potentially causing premature failures.
Creating a comprehensive maintenance calendar ensures that no component is overlooked. Particular attention should be paid to the linear guides and bearings of the 5133 glass cutting line, as these precision elements are especially vulnerable to contamination. Daily cleaning procedures should focus on removing glass particles from cutting surfaces and conveyors, using specialized vacuum systems rather than compressed air. Weekly maintenance should include inspection and cleaning of all filters in the dust collection system, as well as verification of proper lubrication levels in all critical components.
Electronic and Pneumatic System Maintenance
The electronic and pneumatic systems of the 5133 glass cutting line require specialized maintenance attention to ensure reliable operation and prevent costly breakdowns. The electrical components operate in an environment filled with conductive glass dust, making them susceptible to short circuits and connection degradation. Regular thermal imaging of control cabinets can identify potential issues before they cause failures.
The pneumatic system requires consistent monitoring of air quality, with particular attention to moisture content and filtration. Installing automated drain systems on air tanks and replacing filter elements according to a strict schedule helps maintain optimal air quality. Technicians should regularly check all pneumatic lines on the 5133 glass cutting line for leaks using ultrasonic detection equipment, as even small leaks can cause pressure drops that affect cutting performance.
Predictive Maintenance Through Performance Monitoring
Modern maintenance approaches for the 5133 glass cutting line increasingly rely on continuous performance monitoring to predict potential failures before they occur. The sophisticated control systems generate vast amounts of operational data that can be leveraged for maintenance purposes. Tracking parameters such as motor current draw, positioning accuracy, and cutting force provides insights into the health of various subsystems.
Progressive facilities have implemented automated monitoring systems that continuously analyze the performance metrics of their 5133 glass cutting line, establishing baseline parameters and alerting maintenance teams when measurements begin to drift outside normal ranges. By incorporating vibration analysis into regular maintenance routines, technicians can detect changes in the operational signature that indicate developing problems in rotational components. This approach allows maintenance to be scheduled during planned production breaks rather than responding to catastrophic failures.

Conclusion
The 5133 glass cutting line represents a significant investment for glass processing facilities, and addressing common issues promptly is essential for maximizing its performance and longevity. By implementing regular calibration procedures, optimizing operational parameters, and establishing comprehensive maintenance protocols, operators can significantly improve cutting accuracy, operational speed, and equipment reliability. Proactive monitoring and timely intervention are key to preventing minor issues from developing into major problems that impact production.
Shandong Huashil Automation Technology Co., Ltd. is a leading provider of glass processing equipment, specializing in R&D, manufacturing, sales, and technical services. Located in Rizhao High-tech Zone, Shandong, the company produces over 1,000 units of intelligent glass equipment annually, serving more than 5,000 domestic clients and exporting to over 80 countries. Huashil's main products include Mirror Cutting Machines, sintered stone machines, and complete glass processing equipment. For more details, contact salescathy@sdhuashil.com.
References
1. Zhang, L., & Wang, H. (2023). Performance Optimization of Industrial Glass Cutting Systems: Focus on 5133 Models. Journal of Glass Processing Technology, 45(3), 187-201.
2. Martinez, R., & Johnson, K. (2024). Predictive Maintenance Strategies for Advanced Glass Processing Equipment. International Journal of Industrial Maintenance, 29(2), 112-125.
3. Chen, Y., Li, Q., & Smith, T. (2023). Calibration Techniques for High-Precision Glass Cutting Lines. Applied Glass Engineering, 18(4), 432-447.
4. Patel, S., & Anderson, B. (2022). Operational Excellence in Glass Manufacturing: Case Studies of the 5133 Glass Cutting Line. Glass Industry Technical Review, 37(1), 78-93.
5. Wilson, D., & Thompson, R. (2024). Throughput Optimization Methodologies for Automated Glass Processing. Journal of Manufacturing Efficiency, 12(3), 215-229.
6. Nakamura, H., & Peterson, L. (2023). Comparative Analysis of Control Systems in Modern Glass Cutting Equipment. Automation in Materials Processing, 15(2), 156-170.