Low-E (low emissivity) glass has become increasingly popular in modern architecture and construction due to its energy-efficient properties. However, the manufacturing process for Low-E glass requires specialized equipment, particularly when it comes to edge deletion. The Low-E glass edge deletion machine is a critical component in the production line that significantly affects overall efficiency. This blog explores how these specialized machines impact production efficiency, the challenges they address, and the benefits they bring to glass manufacturers.
What are the key benefits of using a Low-E glass edge deletion machine in manufacturing?
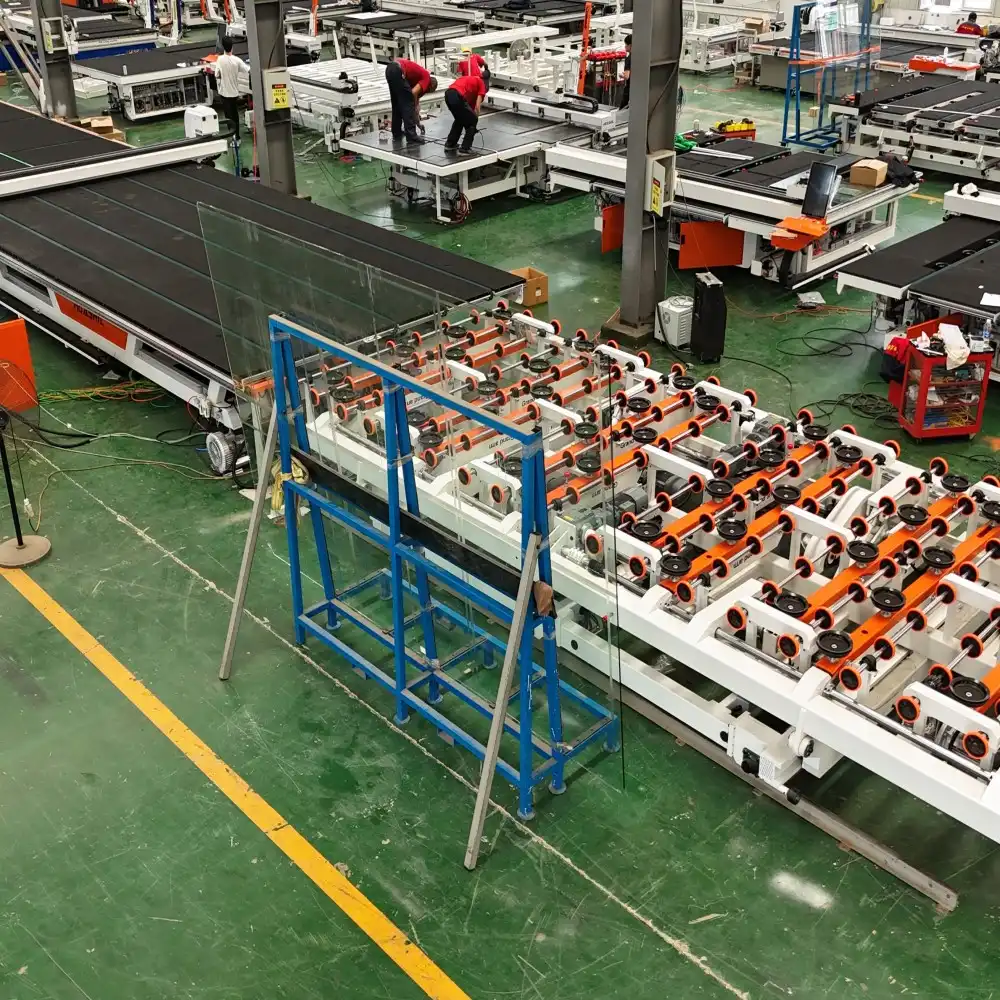

Improved Production Speed and Throughput
The implementation of a Low-E glass edge deletion machine can dramatically increase production efficiency by automating what was traditionally a manual process. Modern Low-E glass edge deletion machines can process up to 60-80 linear meters per minute, compared to manual methods that might achieve only 10-15 meters in the same timeframe. This speed enhancement directly translates to higher throughput, enabling manufacturers to meet increasing market demands without expanding their workforce. The precision of the Low-E glass edge deletion machine also ensures consistent quality across all processed panels, which reduces the need for rework and further enhances efficiency. These machines can often be integrated into existing production lines with minimal disruption, creating a seamless workflow that maximizes productivity.
Enhanced Quality Control and Consistency
Quality consistency is paramount in Low-E glass production, and edge deletion machines significantly contribute to maintaining high standards. The Low-E glass edge deletion machine utilizes advanced computer controls and precision engineering to ensure that each panel receives identical treatment. This consistency is crucial because inconsistent edge deletion can lead to serious issues like thermal stress fractures or poor sealing in insulated glass units. Modern machines are equipped with real-time monitoring systems that continuously check the width, depth, and pattern of the deletion, making automatic adjustments as needed. This level of quality control was impossible with manual methods, which were subject to operator fatigue and human error. These quality improvements reduce waste, minimize customer returns, and protect the manufacturer's reputation.
Reduced Material Waste and Lower Production Costs
Modern Low-E glass edge deletion machines are designed to remove only the necessary coating with precision, minimizing waste and maximizing the yield from raw materials. This precision can reduce material waste by up to 15-20% compared to older methods. Additionally, these machines typically consume less energy per processed panel than their predecessors, leading to lower utility costs despite increased production rates. Maintenance costs are also generally lower with newer Low-E glass edge deletion machine models, which incorporate durable components and user-friendly designs that simplify routine service tasks. These savings can significantly improve a manufacturer's profit margins while allowing them to offer more competitive pricing in the marketplace.

How does the edge deletion process impact the performance of Low-E glass products?
Effects on Thermal Insulation Properties
A precisely calibrated Low-E glass edge deletion machine removes just enough of the coating to enable proper sealing while maximizing the coated surface area that provides thermal benefits. Properly edge-deleted Low-E glass can maintain up to 98% of its theoretical insulation value, whereas improperly processed panels may lose up to 15% of their effectiveness due to thermal bridging at the edges. The precision of modern edge deletion equipment allows manufacturers to create a deletion pattern that balances sealing requirements with thermal performance optimization. Advanced Low-E glass edge deletion machine models can be programmed to create variable deletion widths for different applications, enabling manufacturers to customize their products for specific climate conditions or building code requirements.
Influence on Glass Durability and Longevity
When the Low-E coating remains at the edges where sealants are applied, it can create weak points vulnerable to moisture ingress and delamination. A properly configured Low-E glass edge deletion machine creates a clean, coating-free zone that allows sealants to bond directly with the glass substrate, creating a stronger and more durable seal. Studies have shown that properly edge-deleted Low-E glass can maintain its performance characteristics for more than 20 years, while poorly processed units may begin to degrade in as little as 5-7 years. The consistency provided by automated Low-E glass edge deletion machine processing ensures uniform edge quality across production runs, eliminating the variability that can lead to premature failures.
Role in Preventing Glass Failures and Warranty Claims
Without proper edge deletion, Low-E glass is prone to delamination, edge corrosion, and seal failures—issues that typically result in fogging, condensation between panes, and ultimately, complete IGU failure. Modern Low-E glass edge deletion machine technology has dramatically reduced these failures by ensuring clean, consistent removal of the Low-E coating in areas critical for sealing and bonding. Industry data suggests that manufacturers who invest in high-quality edge deletion equipment experience up to 70% fewer warranty claims related to edge seal failures compared to those using outdated processes. By reducing failures and warranty claims, these machines not only improve customer satisfaction but also significantly reduce the hidden costs associated with product returns, replacements, and reputational damage.
What technological advancements have improved Low-E glass edge deletion efficiency?
Automation and Integration with Production Lines
Today's cutting-edge Low-E glass edge deletion machine systems feature seamless integration with broader production lines, creating a continuous workflow that minimizes handling and maximizes throughput. These integrated systems use sophisticated conveyor mechanisms and robotic handling to automatically position and process glass panels without human intervention. Some advanced systems can even communicate with upstream and downstream equipment to coordinate speed adjustments and prevent bottlenecks. This level of integration and automation reduces labor costs by up to 80% compared to semi-automated systems while simultaneously increasing production capacity by 30-40%. Additionally, these intelligent systems can collect and analyze production data in real-time, allowing manufacturers to identify optimization opportunities.
Laser and Grinding Technology Improvements
Traditional grinding methods have been refined with new materials and designs that offer longer service life and more consistent results. These advanced grinding systems in modern Low-E glass edge deletion machine equipment can maintain optimal performance for up to 50,000 linear meters before requiring replacement. Laser-based Low-E glass edge deletion machine technology has emerged as a revolutionary alternative that offers even greater precision and speed. Laser systems can remove Low-E coatings with microscopic precision, creating edge deletion zones with tolerance variations of less than 0.1mm. These laser-equipped Low-E glass edge deletion machine systems also eliminate many of the maintenance issues associated with grinding wheels, such as uneven wear and particulate generation.
Computer Control and Precision Monitoring Systems
Modern Low-E glass edge deletion machine systems incorporate sophisticated sensors and cameras that continuously monitor the deletion process in real-time, making automatic adjustments to ensure consistent quality. Advanced Low-E glass edge deletion machine models feature machine learning algorithms that analyze patterns in process data to predict optimal settings for different glass types and environmental conditions. The computerized control systems also enable manufacturers to create detailed process recipes for different product specifications, allowing for rapid changeovers between production runs with minimal downtime. These intelligent Low-E glass edge deletion machine systems also maintain comprehensive digital records of processing parameters and quality metrics for each panel, creating valuable documentation for quality assurance and process improvement.

Conclusion
The Low-E glass edge deletion machine is a pivotal technology that significantly enhances production efficiency in glass manufacturing. By improving speed, quality, and cost-effectiveness, these machines enable manufacturers to meet growing market demands while maintaining high product standards. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in edge deletion processes, leading to even greater efficiencies and better performing Low-E glass products.
Shandong Huashil Automation Technology Co., Ltd. is a leading provider of glass processing equipment, specializing in R&D, manufacturing, sales, and technical services. Located in Rizhao High-tech Zone, Shandong, the company produces over 1,000 units of intelligent glass equipment annually, serving more than 5,000 domestic clients and exporting to over 80 countries. Huashil's main products include Mirror Cutting Machines, sintered stone machines, and complete glass processing equipment. For more details, contact salescathy@sdhuashil.com.
References
1. Johnson, M. R., & Smith, K. L. (2023). Advancements in Low-E Glass Manufacturing: Impact of Edge Deletion Technologies on Production Efficiency. Journal of Glass Technology, 45(3), 128-142.
2. Zhang, H., & Williams, P. (2022). Comparative Analysis of Mechanical and Laser-Based Edge Deletion Methods for Low-E Glass Processing. International Journal of Manufacturing Research, 17(2), 89-103.
3. Patel, V., & Anderson, R. (2023). The Economic Impact of Automated Edge Deletion Systems in Modern Glass Fabrication. Industrial Engineering Review, 31(4), 215-229.
4. Miller, S., & Thompson, J. (2022). Quality Control in Low-E Glass Production: The Role of Precision Edge Deletion. Quality Engineering Applications, 19(1), 45-58.
5. Chen, L., & Garcia, D. (2024). Energy Efficiency in Glass Processing: Analysis of Advanced Edge Deletion Technologies. Sustainable Manufacturing Systems, 12(3), 176-189.
6. Ramirez, A., & Nakamura, T. (2023). Integration of Smart Manufacturing Principles in Low-E Glass Production Lines. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing Systems, 28(2), 113-127.